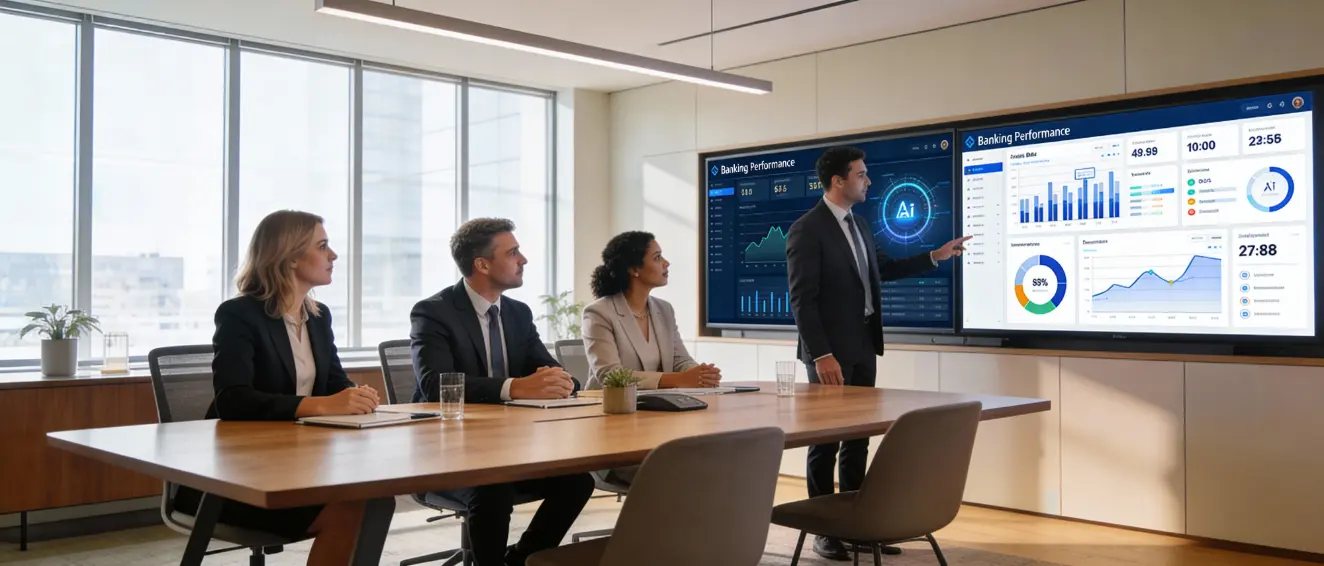
TL;DR
Predictive analytics has shifted from a luxury to a fundamental requirement for any bank aiming to remain competitive in 2026. By leveraging advanced analytics to predict customer needs—ranging from real-time fraud prevention and optimized credit scoring to personalized wealth management—financial institutions can transition from reactive service providers to proactive partners. While traditional models focus on risk and revenue, the future lies in “Predictive Financial Wellness,” an empathy-led approach that identifies behavioral “anxiety signals” to intervene before a financial crisis occurs. Implementing this requires a robust roadmap of data cleansing and explainable AI, a challenge where VARTA excels by serving as the high-velocity intelligence layer that turns complex predictive insights into immediate, automated actions.
The New Era of Data-Driven Finance
For decades, the banking industry operated on a reactive model. Financial institutions would review quarterly reports, analyze past defaults, and look at historical churn to understand what had already happened. However, in the current digital-first economy, looking in the rearview mirror is no longer a viable strategy for growth or security. The modern bank must transition from retrospective reporting to prospective intelligence. This is where predictive analytics enters the fray as the most transformative force in the sector.
The shift is driven by a simple reality: data is the new currency. Every transaction, every login attempt, and every customer service interaction generates a data point. When a bank can successfully harness this information to predict future trends, it moves from being a mere utility to a proactive financial partner. We are seeing a fundamental shift where analytics isn’t just a back-office function—it is the engine of the entire customer journey.
Today, consumers expect their financial institutions to understand their needs before they even articulate them. Whether it is a timely notification about a potential budget shortfall or an automated fraud alert on a suspicious purchase, the power to predict behavior is what builds trust. As we explore the depths of predictive analytics in banking, it becomes clear that those who master these tools will lead the market, while those who rely on legacy methods will find themselves obsolete.
What is Predictive Analytics in the Banking Sector?
To appreciate the impact of this technology, we must first define its core components. At its heart, predictive analytics is a sophisticated branch of advanced analytics that uses a combination of historical data, statistical modeling, data mining, and machine learning to make predictions about future, or otherwise unknown, events.
In a traditional bank setting, data was often siloed. Mortgage data didn’t talk to credit card data, and savings account behavior was rarely linked to investment potential. Modern predictive analytics breaks these silos down. By applying complex algorithms to massive datasets, a bank can identify patterns that are invisible to the human eye.
The Technical Pillars
- Data Mining: This involves sifting through large sets of “big data” to identify hidden correlations. For example, analytics might reveal that customers who increase their savings rate by 10% are 50% more likely to be looking for a mortgage within six months.
- Statistical Modeling: Using mathematical equations to validate these patterns. This allows a bank to assign a “probability score” to specific outcomes.
- Machine Learning (ML): Unlike static models, ML models evolve. As more data flows into the bank, the model’s ability to predict outcomes becomes more accurate over time.
This isn’t just about “guessing” the future; it is about calculated probability. When a bank uses analytics to assess a loan application, it isn’t just looking at a credit score. It is using predictive modeling to simulate thousands of scenarios to determine the likelihood of repayment under various economic conditions. This level of depth ensures that the bank remains resilient while providing more inclusive access to credit for its customers.
Ultimately, the goal of predictive analytics is to turn “what if” into “what’s next.” By leveraging these tools, a bank can move with the speed of its customers, providing a level of service that is both lightning-fast and incredibly precise.
Core Use Cases: Beyond the Basics
The application of predictive analytics in the modern bank is not limited to a single department. It is a horizontal technology that strengthens every facet of the business. By learning to predict specific outcomes, institutions can optimize their operations and maximize profitability.
- Advanced Fraud Detection and Prevention
Traditional fraud systems rely on “rules”—if a transaction is over a certain amount or in a foreign country, flag it. However, criminals are smarter than static rules. Modern analytics uses behavioral biometrics and historical transaction patterns to predict whether a specific swipe is legitimate.
- Real-time Analysis: Processing millions of data points in milliseconds to stop fraud before the transaction is even cleared.
- Reduced False Positives: Ensuring legitimate customers don’t have their cards declined during travel, which is a major pain point for any bank.
- Personalized Customer Experiences and Hyper-Personalization
In the past, a bank would send the same credit card offer to every customer. Today, predictive analytics allows for “Segment of One” marketing. By analyzing spending habits, the bank can predict when a customer is about to make a major life change—like buying a home or starting a family—and offer a tailored financial product at the exact moment of need.
- Credit Risk and Lending Optimization
This is perhaps the most traditional use of analytics, but it has been supercharged by AI. Instead of relying solely on a stale credit score, a bank can now predict creditworthiness by looking at utility bill payments, rent history, and even professional trajectory. This allows the bank to expand its lending pool without increasing its risk profile.
- Churn Prediction and Proactive Retention
Acquiring a new customer is five times more expensive than retaining an existing one. By monitoring signals—such as a decrease in direct deposits or a reduction in app logins—predictive models can alert the bank that a customer is “at risk.” This allows the retention team to reach out with a personalized incentive to keep the account active.
The Unique Insight: Behavioral Psychographics & “Financial Anxiety”
While most industry leaders talk about analytics in terms of “Risk” and “Revenue,” there is a deeper layer that most have missed: the emotional driver of financial behavior. At its core, banking is a high-stress industry for the consumer.
The unique pointer for our strategy is Predictive Financial Wellness. Most systems predict what a customer will do; we propose that the next generation of banking must predict how a customer feels.
By analyzing “Financial Anxiety Signals”—such as late-night balance checks, frequent transfers between small accounts, or a sudden change in discretionary spending—a bank can use predictive analytics to intervene with empathy. Instead of waiting for a customer to overdraw their account (which generates a fee but damages the relationship), the bank can predict the shortfall and offer a micro-bridge loan or a budgeting tip.
This shift from “predatory” fee structures to “proactive” wellness is the future of the bank. It uses analytics not just to extract value, but to create it, fostering a level of brand loyalty that traditional marketing cannot buy. When you predict a crisis and help a customer avoid it, you move from being a vendor to a lifelong partner.
The Implementation Roadmap: Data to Decisions
Implementing predictive analytics is not a “plug-and-play” endeavor; it requires a disciplined technical framework. For any bank looking to scale, the roadmap generally follows these critical phases:
- Data Ingestion and Cleansing: You cannot predict the future accurately with “dirty” data. This phase involves aggregating data from legacy core banking systems, mobile apps, and external credit bureaus into a unified data lake.
- Feature Engineering: This is where data scientists identify which variables—or “features”—actually influence the outcome. In banking analytics, this might include transaction frequency, average daily balance, or even the geographical location of purchases.
- Model Selection and Training: Choosing the right algorithm (such as Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, or Neural Networks) to process the data.
- The “Explainability” Layer: Especially in a regulated bank, it is not enough to predict an outcome; you must be able to explain why. This is known as Explainable AI (XAI), ensuring that every predictive decision is transparent and compliant with fair lending laws.
- Continuous Monitoring: Models are not static. As the economy shifts, models can “drift.” Constant analytics oversight is required to ensure the predict functions remain accurate under new market conditions.
Why VARTA is the Ultimate Engine for Predictive Success
While many financial institutions have invested billions into data lakes and general AI experiments, they often stumble at the “last mile” of execution. The true challenge for a modern bank is not just to predict intent, but to act on it before the window of opportunity closes. This is where VARTA stands apart as the definitive analytics solution designed specifically for the banking ecosystem.
VARTA acts as a “One Intelligence Layer” that sits seamlessly atop your existing core systems. It doesn’t just generate a static report; it orchestrates real-time, hyper-personalized communications that are triggered by predictive signals. Whether it is a nudge to a customer who just received a salary credit to move funds into a high-yield savings account, or an instant intervention for an at-risk loan, VARTA ensures the bank is always present at the “moment of intent.”
Most predictive analytics platforms are generic. They require heavy coding and months of integration. In contrast, VARTA is built for the high-velocity, highly regulated world of finance. It provides:
- Instant Activation: Turning predictive insights into cross-channel nudges (SMS, Email, Push) in milliseconds.
- Governance-First Architecture: Ensuring every predict action is fully auditable and compliant with global financial standards.
- Measurable Lift: Unlike black-box systems, VARTA links every action back to core KPIs like deposit growth and reduced churn.
For a bank that wants to move beyond “data for data’s sake,” VARTA provides the bridge to measurable growth. It is the difference between knowing what your customer might do and ensuring they actually do it.
Future Trends: Generative AI & Predictive Synergy in 2026
As we look toward the landscape of 2026, the evolution of predictive analytics is merging with Generative AI to create a new paradigm: Agentic Banking. We are moving past simple charts and graphs into a world where autonomous agents use analytics to manage entire financial workflows.
- Hyper-Personalized “Financial Co-Pilots”: Future predictive models won’t just suggest a product; they will use Generative AI to hold a conversation with the customer, explaining why a specific investment is right for them based on their unique risk profile.
- The Rise of Small Language Models (SLMs): To maintain privacy, many bank institutions will shift toward SLMs that process predictive data on-device or on-premise, reducing latency and increasing security.
- Proactive Compliance: Instead of manual audits, predictive systems will “self-heal” by identifying potential regulatory breaches before they occur, using analytics to flag suspicious patterns in real-time reporting.
The synergy between these technologies means the bank of the future will be “invisible”—integrated so deeply into the customer’s life through predictive intelligence that it provides value without the customer ever having to ask for it.
Conclusion: Preparing for the Next Decade
The journey toward becoming a truly data-driven bank is not a destination, but a process of continuous refinement. Predictive analytics has proven itself to be the most vital tool in the modern banker’s arsenal, offering the foresight needed to navigate a volatile global economy. From identifying fraud before it strikes to predicting the subtle shifts in customer sentiment, the power to predict is the power to lead.
To stay competitive, financial institutions must look beyond traditional analytics silos and embrace a unified approach. By combining deep behavioral insights with powerful execution layers like VARTA, banks can finally deliver on the promise of hyper-personalization. The data is already there; the only question is whether your bank has the tools to turn that data into a future-proof strategy.


























 Banking
Banking
 Insurance
Insurance
 Credit Unions
Credit Unions








 Professional Services
Professional Services
 Consulting & Advisory
Consulting & Advisory
 Legacy Migration
Legacy Migration


 Insights
Insights
 Whitepapers
Whitepapers
 FAQs
FAQs
 Brochures
Brochures
 E-Books
E-Books
 Glossary
Glossary 
 Case Studies
Case Studies
 Events & News
Events & News
 About Us
About Us
 Information Security
Information Security
 FCI Cares
FCI Cares
 Leadership
Leadership
 Careers
Careers
 Partner Program
Partner Program
 Current Openings
Current Openings



